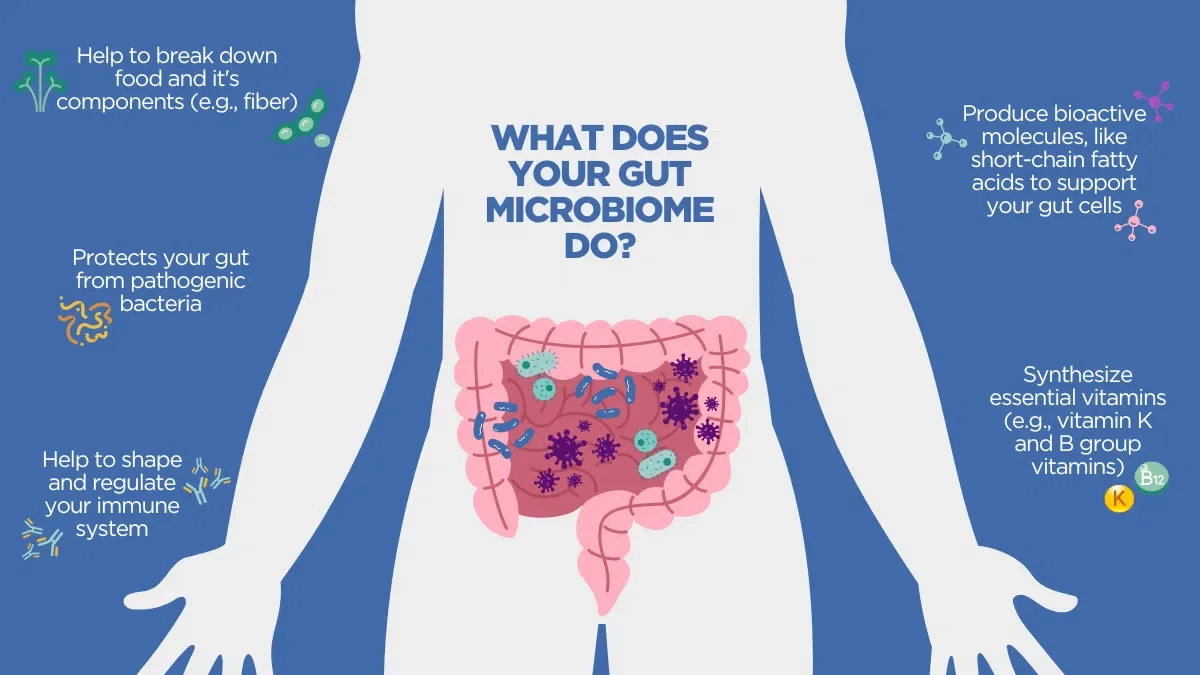
What is gut microbiome?
A microbiome is the community of microorganisms that live in the gut, including “100 trillion bacteria, including beneficial and pathogenic strains”(Guy, 2025), and when they are balanced, they contribute greatly to overall health. These microbes help break down foods the body cannot digest alone, producing “short-chain fatty acids that support gut health” (Guy, 2025), while also supporting the immune system and helping prevent harmful invaders from taking over. They influence metabolism by assisting with blood sugar control and hunger regulation, and they produce essential nutrients such as “vitamin K2” and “B12” (Guy, 2025).
The microbiome also supports detoxification by helping process medications and environmental chemicals, preventing excess buildup in the body. Just as importantly, it plays a strong role in mental wellbeing through the gut–brain connection, often referred to as “the second brain”(Guy, 2025), where many mood-related chemicals “such as serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, are produced in the gut” (Guy, 2025) showing that a healthy mind and a healthy gut work closely together.